 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-3010-94
7.0 Application Examples; Dissolving Operations Examples
The main value of the release estimates is again the indication that the unmitigated
consequences from the oxide dissolution are low and, accordingly, worker safety is the
principle focus of concern. This is an important perspective that, again, may be useful in
applying a graded approach to facility management.
7.3.3 Residue Dissolution
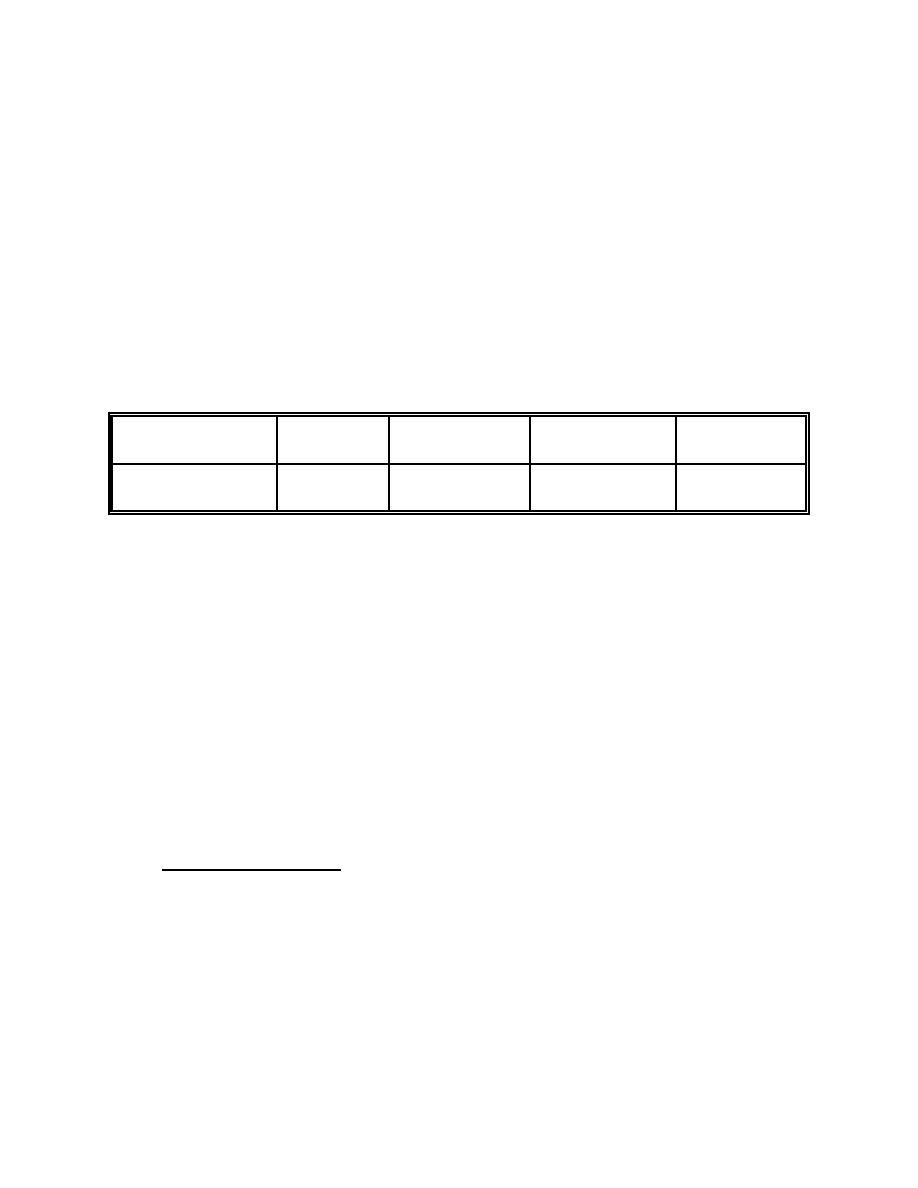
Release topics explored in this example are listed in Table 7-6.
Table 7-6. Residue Dissolution Example Topics
Liquid
Metal
Powder
Surface
Criticality
- Venting of
- N/A
- N/A
- None
- None
pressurized liquids
7.3.3.1
Hazard Summary
This activity receives, via a conveyor, residues heavily contaminated with plutonium that
have been reduced in size in the feed preparation operation. This material is placed in a feed
hopper that slowly feeds it into the nitric acid dissolver, after which only liquid materials are
handled. This operation is virtually identical to the oxide dissolution operation previously
described. The only new complication in residue dissolution is the need for a screw feed
conveyor to prevent an excessive dissolution rate of residue impurities from causing an
eructation in the dissolver vessel.
7.3.3.2
Release Estimation
The only new potential energetic phenomenon is an eructation from the dissolver vessel due
to an excessive impurity feed rate.
A. Dissolver Eructation. The dissolution process is a batch operation. The
maximum feed allowed in any one batch is 1000 g as plutonium. The maximum
release is obtained if the eructation occurs when the majority of the plutonium has
been fed to the dissolver. The eructation is a relatively low pressure phenomena, and
any gas backleakage through the material-filled conveyor would have almost no effect
on the feed residue. For an initial bound, a DR of 1.0 is conservatively assumed.
Small eructations are handled by the vessel vent system. A larger eructation can
drive gas into the glovebox. In a worst case, the dissolver blowout plug may fail,
Page 7-19
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |