 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-1129-99
70.00
60.00
M%He3At-t
m% He3
M%DTAt-t
50.00
M%D2At-t
M%ArAt-t
40.00
m% DT
30.00
m% AR
20.00
m% D2
10.00
0.00
0.000
6.162
12.323
18.485
24.646
30.808
36.969
43.131
49.292
55.454
61.615
67.777
73.938
Elapsed Time In Increments Of 1/4 Half Life
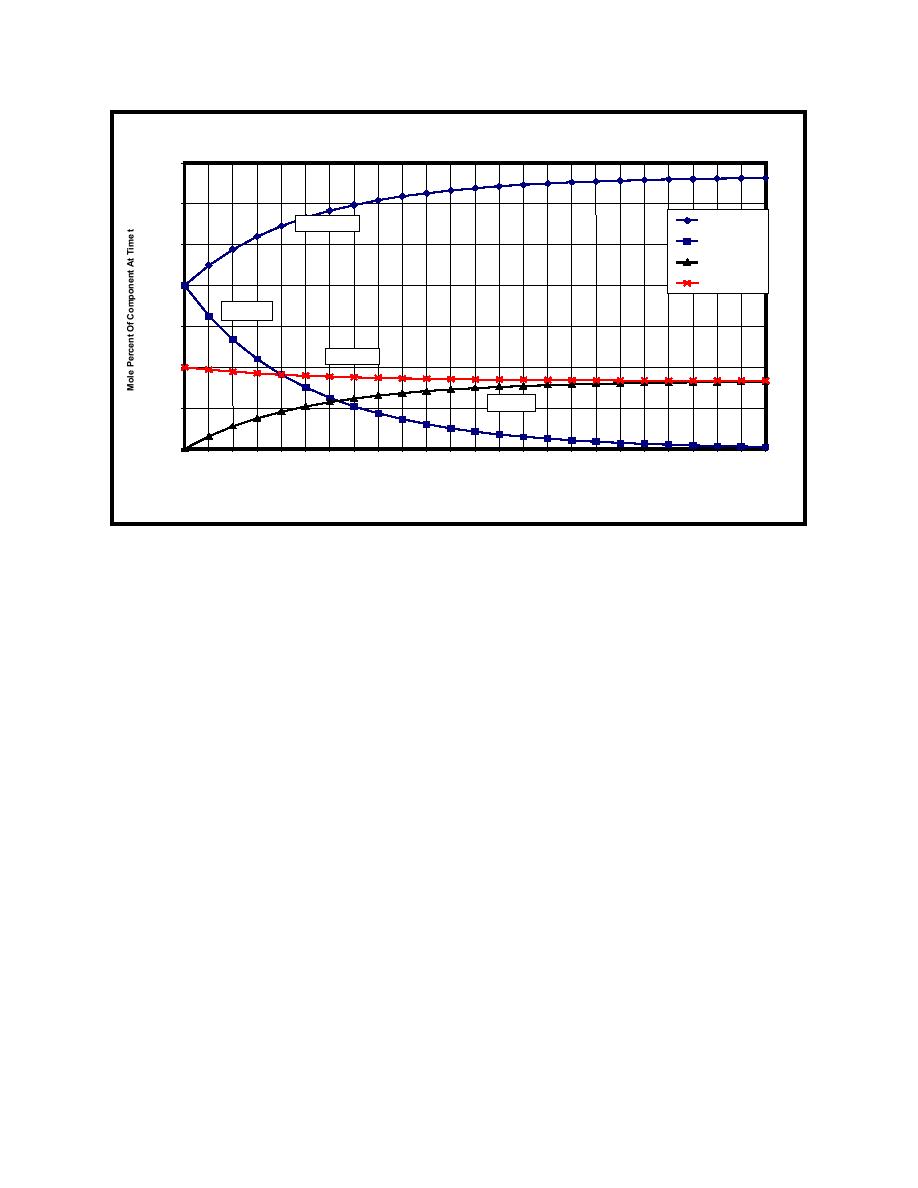
FIGURE C-6. 40% DT, 40% 3He, and 20% Ar, Change in mole percent
of each component versus time
C.3 Calorimetry Assay
Calorimetry is the quantitative measurement of heat. A calorimeter is an apparatus for
measuring heat quantities generated in or emitted by materials in processes such as chemical
reaction, changes of state, and formation of solutions. Heat is generally measured in calories or
joules. A calorie is a unit of heat energy equal to the heat energy required to raise the
temperature of a gram of water from 14.5 to 15.5oC, at a constant pressure of 1 atmosphere. A
calorie is equal to 4.186 joules.
A calorimeter designed to be used in processes that continually generate heat (power sources)
and measures power instead of heat is called a Constant Heat Flow (CHF) calorimeter. A CHF
calorimeter measures the power (joules/second) of a source not the heat output (joules) of a
source. The power is usually measured in Watts, which is a unit of power equal to 1
joule/second.
A radioactive material is a power source, which deposits the energy due to decay in the
radioactive material itself and in the materials surrounding the radioactive material. The power
generated by the decay of tritium has been measured and is equal to 0.3240 0.0009
Watts/gram of tritium.
Mound Laboratory has been the leader in the design, fabrication, calibration, and operation of
CHF calorimeters for many years. Mound has specialized in the development of CHF
calorimeters to be used in the measurement of radioactive material quantities by measuring
their power output. CHF calorimeters are generally designed to meet the specific needs of the
items to be assayed and are limited in application by the following:
C-12
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |