 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-1129-99
The contribution to dose from bremsstrahlung has been estimated. [2-3] Although this contribution
is probably relatively small, it should be considered in the evaluation of lung doses from significant
intakes of tritiated particulates.
Recently, estimates of effective doses from inhalation of various types of tritiated particulates were
made [4]. These estimates are based on in-vitro and animal (rat) studies with titanium tritide. The
assumption is made that the tritium, once dissolved, has the same distribution and retention as
HTO in the body. The dose conversion factors (DCF) calculated for such intakes in adults are
listed in Table 2-2.
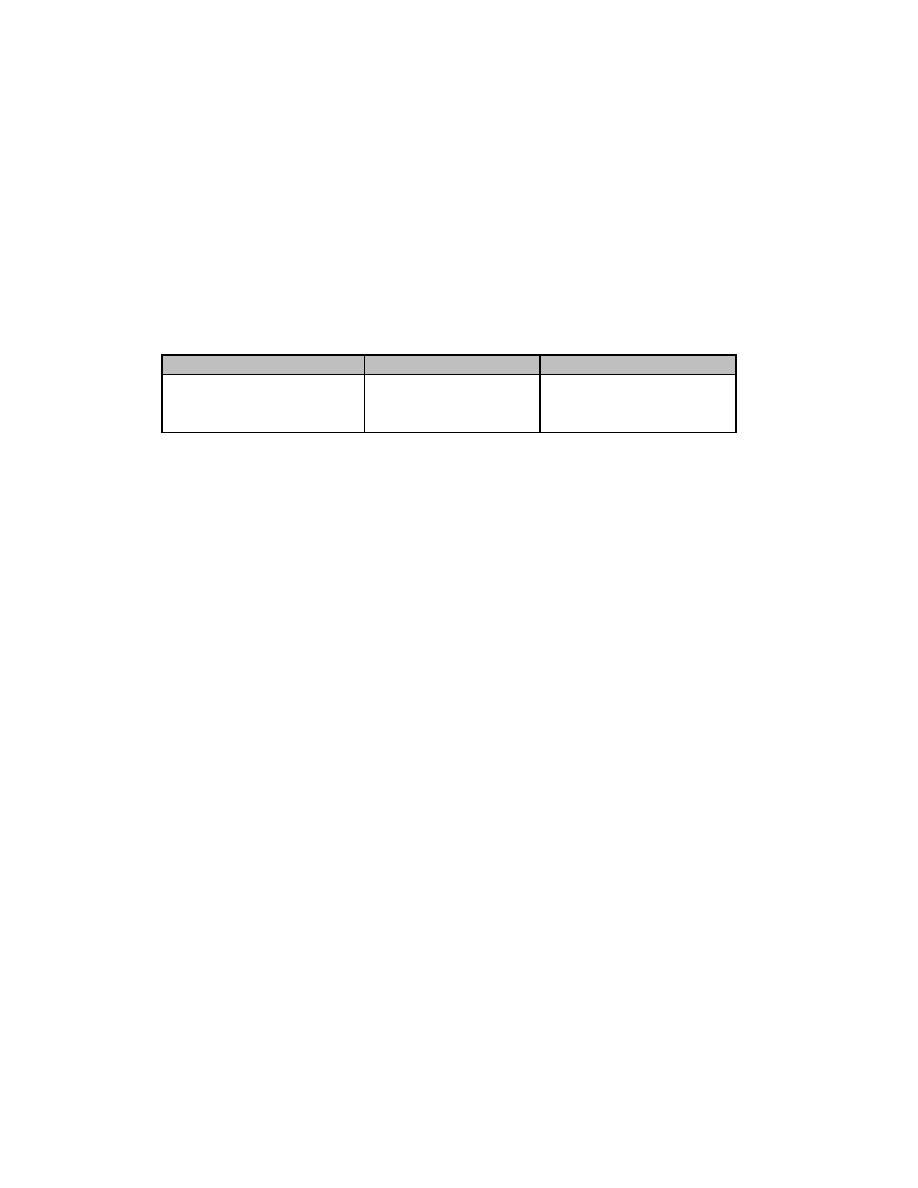
TABLE 2-2. ICRP-71 dose conversion factors for
inhalation of tritiated particulates
Lung Absorption Type* DCF (Sv/Bq inhaled) DCF (rem/Ci inhaled)
Fast
6.2 E-12
2.3 E-05
Moderate
4.5 E-11
1.7 E-04
Slow
2.6 E-10
9.6 E-04
*Based on ICRP-66 Respiratory Tract Model and ICRP 60 Tissue Weighting Factors
The dose from inhalation of tritiated particulates must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis. In
general, as with any suspected intake of tritium, urine samples should be collected. In the event of
a suspected significant exposure of tritiated particulates, collection of early (first few days) fecal
samples should be considered. Inhaled particulates are expected to be eliminated via this route.
Cases involving inhalation of metal tritides have occurred in which significant tritium was seen in
the feces, but not in the urine [5]. Collection and analysis of fecal samples (analysis based on
fecal sampling must be cognizant of particle matrix absorption effects) allows confirmation of intake
and may give information regarding the fractional uptake.
2.5 Preferred Forms
Most tritium in the DOE complex exists as a gas, in the form of tritiated water, or as a metal tritide.
The preferred form of tritium is dependent upon its use in a process, length of storage, or its
classification as a waste.
2.5.1 Characterization of Tritium Forms
2.5.1.a Gaseous Tritium
The use, transfer, storage, and shipment of gaseous tritium at or near atmospheric pressure has a
long history in the DOE complex and has been safely used for over thirty years. Gaseous tritium at
or near atmospheric pressure occupies 22.414 L/mole at 0 C, and approximately 24.2 L/mole at
room temperature, and requires approved packages for shipment in either Type A or B quantities.
If the containers are not properly designed or if they are damaged, the gas can leak from the
container into the environment.
Gaseous tritium at ambient pressure is easily handled by most gas handling systems and is a good
source for general-purpose use. At low pressure and temperature, the tritium does not penetrate
deeply into the container wall. Helium and tritium embrittlement of the container wall is not a
significant issue at low pressures even after several years of exposure. As tritium decays, the
pressure in the container increases (see Figure 2-2) due to the generation of the monatomic gas
7
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |