 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Table 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of Plutonium |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|  Radiological Safety Training for Plutonium Facilities
DOEHDBK11452001
Student's Guide
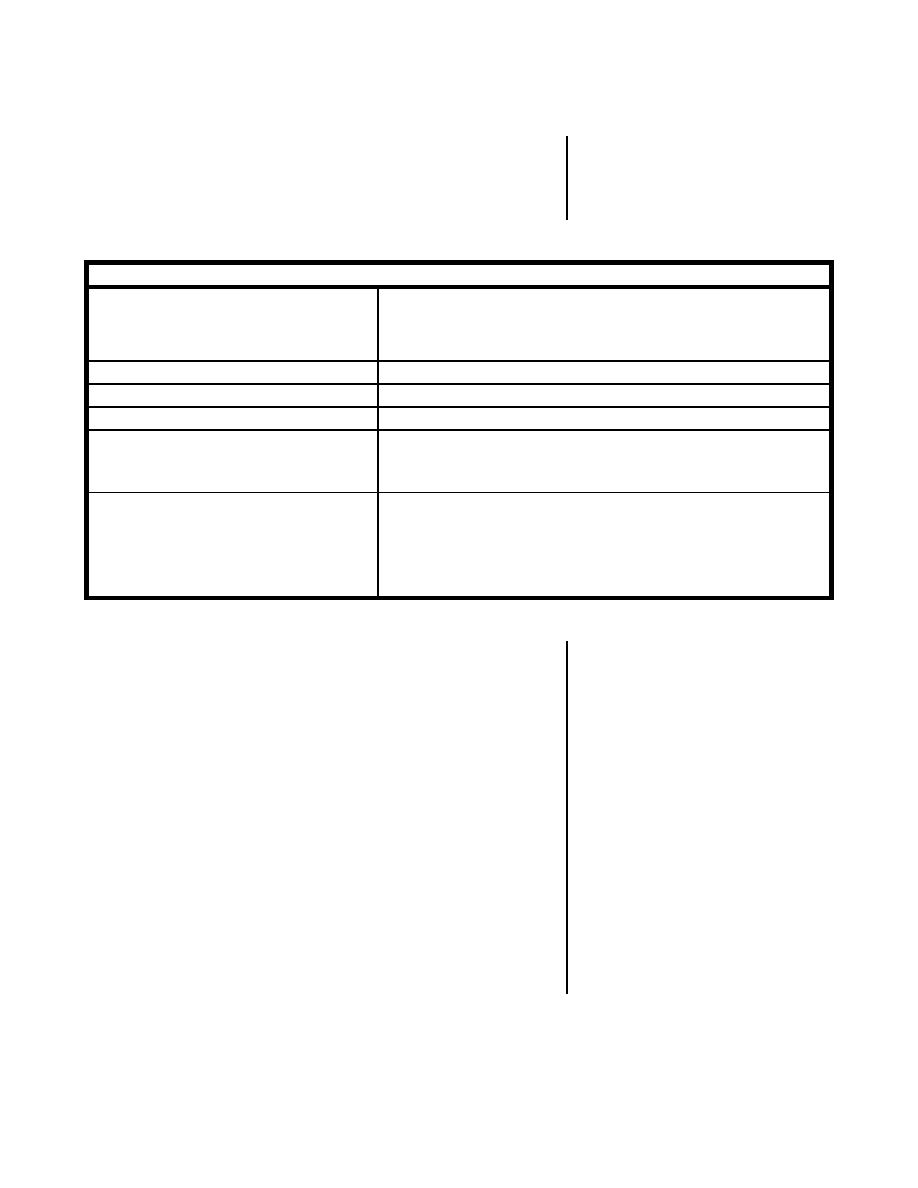
Table 2 contains a brief summary of some of the
features of this metal.
Table 2
Physical and Chemical Properties of Plutonium
3
Density
15.9-19.9 g/cm , depending on metal phase. Loose
3
PuO2 powder has a density of about 2 g/cm , and
3
sintered pellets have a density of 10.3-11.0 g/cm .
640 C
Melting point (pure metal)
Up to 2000 C; varies with alloy.
3327 C
Boiling point (pure metal)
Slow in dry air. Rapid under moist conditions or
Oxidation rate
when heated. May result in a low spontaneous
ignition temperature.
Dissolves readily in concentrated hydrochloric,
Action of acids and bases
hydriodic, and perchloric acids. Attacked by most
dilute acids; not readily attacked by concentrated
sulfuric and nitric acids or sodium hydroxide
solutions.
B. Reactivity
Plutonium metal has proven to be quite pyrophoric
under certain conditions. It reacts with oxygen very
slowly in dry air, but rapidly in moist conditions, or
when the metal is heated.
A pyrophoric reaction can happen with larger
pieces of plutonium; however, fire is more likely to
occur when the plutonium is in a more dispersed form,
such as chips, powder, or turnings. For this reason, it
is handled in a moisture-free (dry air) or oxygen-free
(inert) atmosphere. Note: With an atmosphere that
contains only 5% oxygen, the metal will burn easily.
However, when the oxygen content is reduced to 1%,
a fire will not continue to burn unless heat is supplied.
7
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |