 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Module 101 Properties of Uranium |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-1113-98
Module 101 Properties of Uranium
Lesson Plan
Instructor's Notes
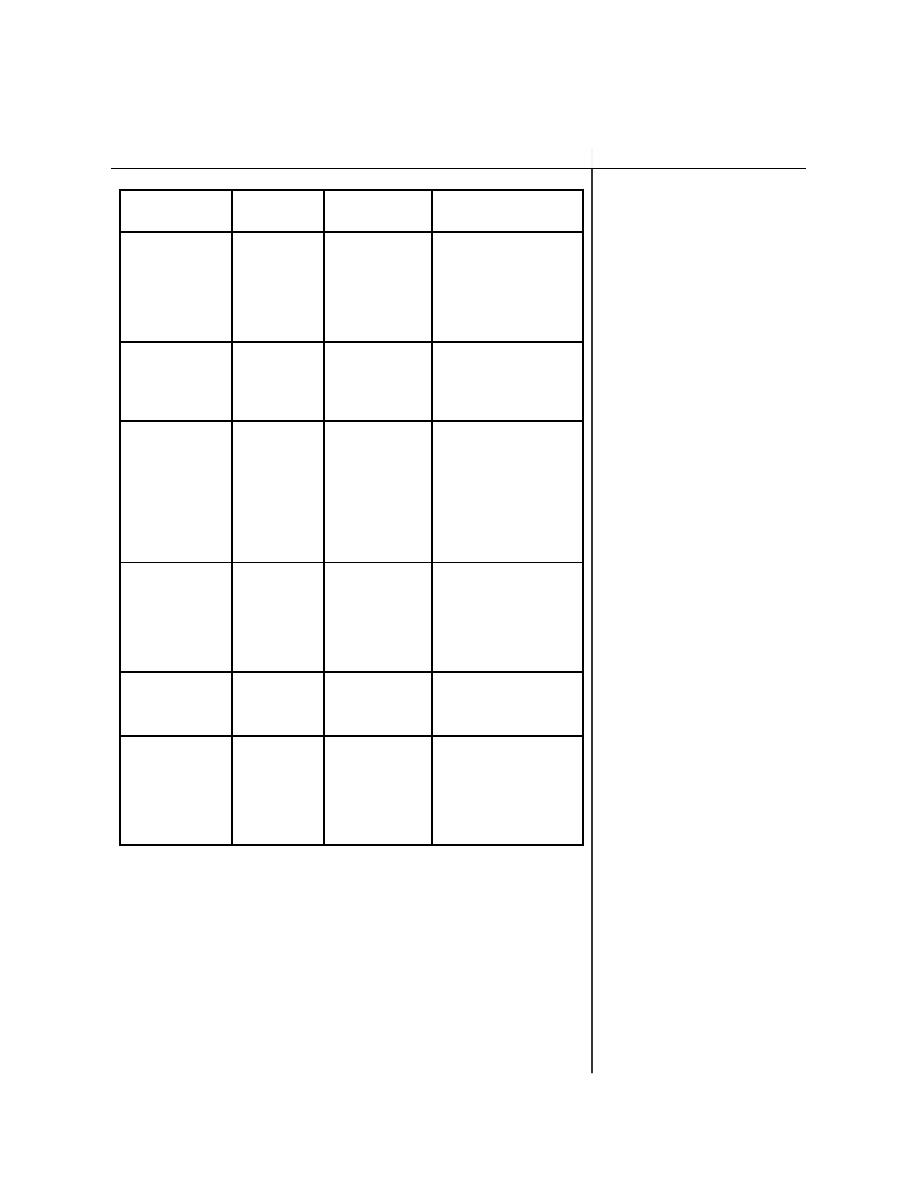
ISOTOPE
HALF-
NAT
IMPORTANCE
LIFE
ABUND
An unwanted byproduct
of 233U production in a
70 y
0%
breeder reactor. Due to
232
U
its much shorter half-
life, 232U contributes
most of the radioactivity
in samples of 233U.
Manufactured by
irradiating 232Th with
233U
1.6 x 10 5 y
0%
neutrons. It is a
criticality hazard
because it is fissile.
A decay product of 238U.
It is concentrated with
2.5 x 105 y
0.0055%
235U during enrichment.
234U
Highly enriched
uranium contains about
1% 234U. Most of the
radioactivity of enriched
uranium is from the
234U.
Fissile with slow
neutrons; therefore, it is
7.1 x 108 y
~0.7%
of primary interest for
235U
reactors and weapons. If
not handled safely, an
accumulation of 235U
could become critical.
Some 235U is converted
2.3 x 107 y
0%
to 236U in reactors. It is
236U
also present in
reprocessed reactor fuel.
The most abundant
uranium isotope. It is
fissionable with fast
neutrons; however, it is
238
U
4.5 x 109 y
~99.3%
not fissile (i.e., with
thermal neutrons) so it is
not a criticality hazard.
10
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |