 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-3010-94
7.0 Application Examples; Liquid Storage and Ion Exchange Examples
7.3.5 Liquid Sampling and Tank Farm
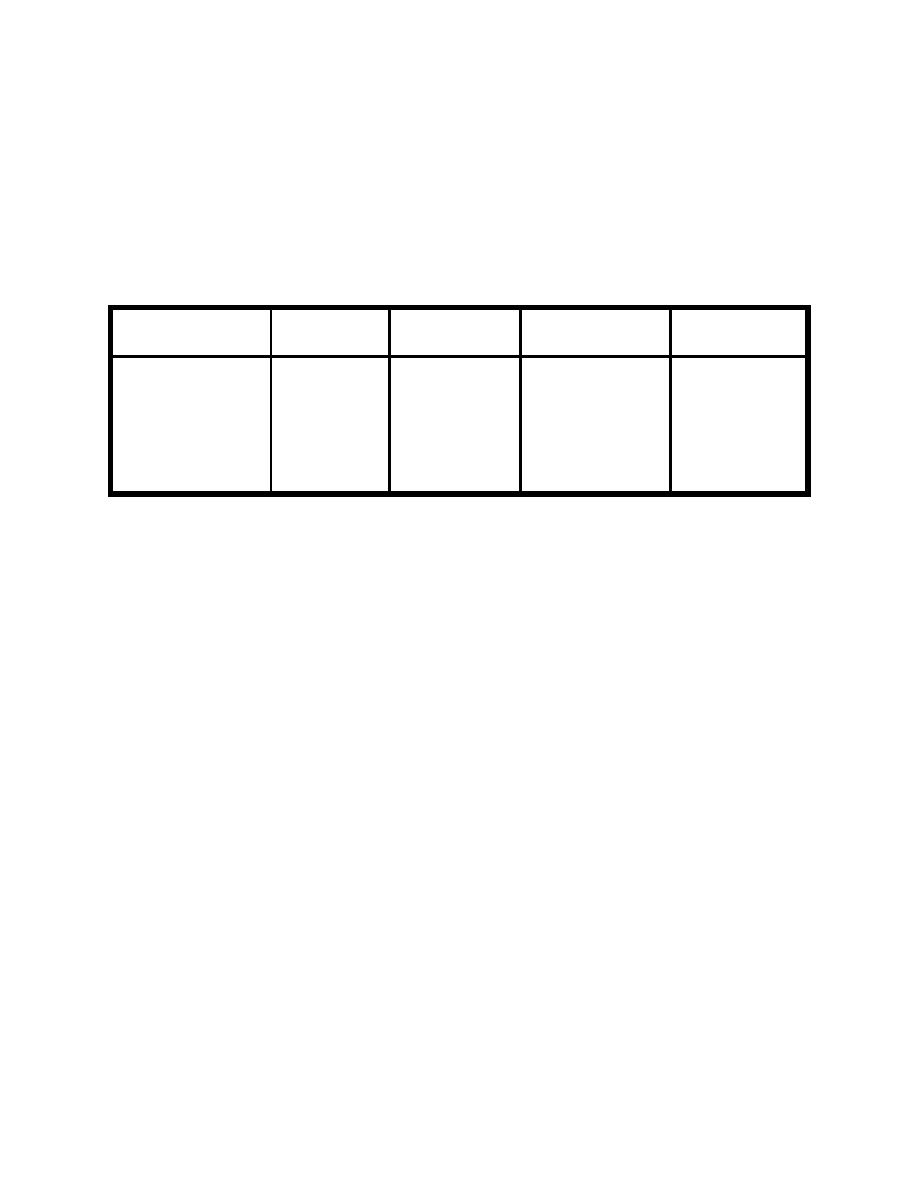
Release topics explored in this example are listed in Table 7-8.
Table 7-8. Liquid Sampling and Tank Farm Example Topics
Liquid
Metal
Powder
Surface
Criticality
- Thermal stress
- N/A
- N/A
- None
- None
- Venting liquid
below surface
level
- Venting
superheated liquid
- Free-fall spill
7.3.5.1
Hazard Summary
This activity involves only liquid material. Plutonium process and liquid waste solutions are
stored in annular tanks in three small rooms located on the west wall of the wet processing
line maintenance room. These tanks receive solution and transfer it to gloveboxes via small
gear pumps. The sample glovebox, located adjacent to the tank storage areas, uses small
centrifugal pumps to circulate and sample tanks. The tanks are equipped with ever open
vents to the vessel vent system and pressure relief lines leading to a raschig ring sump.
Other than pump discharge fluid pressure of 0.14 MPa (20 psia), the major energy source in
the area is a branch-line from the 0.45 MPag (65 psig) instrument air main for remote
operation of tank inlet and outlet valves.
The tanks are geometrically favorable, not geometrically safe, so a solution criticality is
possible. Specific mitigation features include the raschig ring sump for spills and, for
misrouting of material, a relatively common annular design so that any one tank can hold the
maximum flowsheet plutonium concentration while remaining subcritical. Leaks and spills
are possible. There is no significant combustible loading in the area, but a large room fire
could boil liquid and potentially pressurize tanks. The hazard evaluation noted that no
documented estimation of tank venting capability had been made with regard to potential
heat fluxes from a fire.
Page 7-28
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |