 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-3010-94
7.0 Application Examples; Reduction Line Example
because it often becomes a mess in a hurry otherwise. Numerous oil stains are
visible on the calciner insulation. Extensive accumulations of tape are visible at
several connection points on the hydraulic lines. A number of outstanding work
requests exist on the unit.
3. The paint on combustible hydrofluorinator shielding is thin and obviously worn
with numerous scratches and chips revealing the underlying material.
Such findings indicate that the integration of operations, maintenance, assessment, etc.,
functions is poor. The proper emphasis and support is not being given to safety management
programs regardless of how much effort is being expended on "safety analysis." On the
other hand, opposite findings would indicate that actual issues are being systematically
addressed in an effective manner. Such considerations are real, directly relevant to the
overall facility safety basis, and not amenable to effective assessment by source term
considerations alone.
7.3.8 Reduction Line
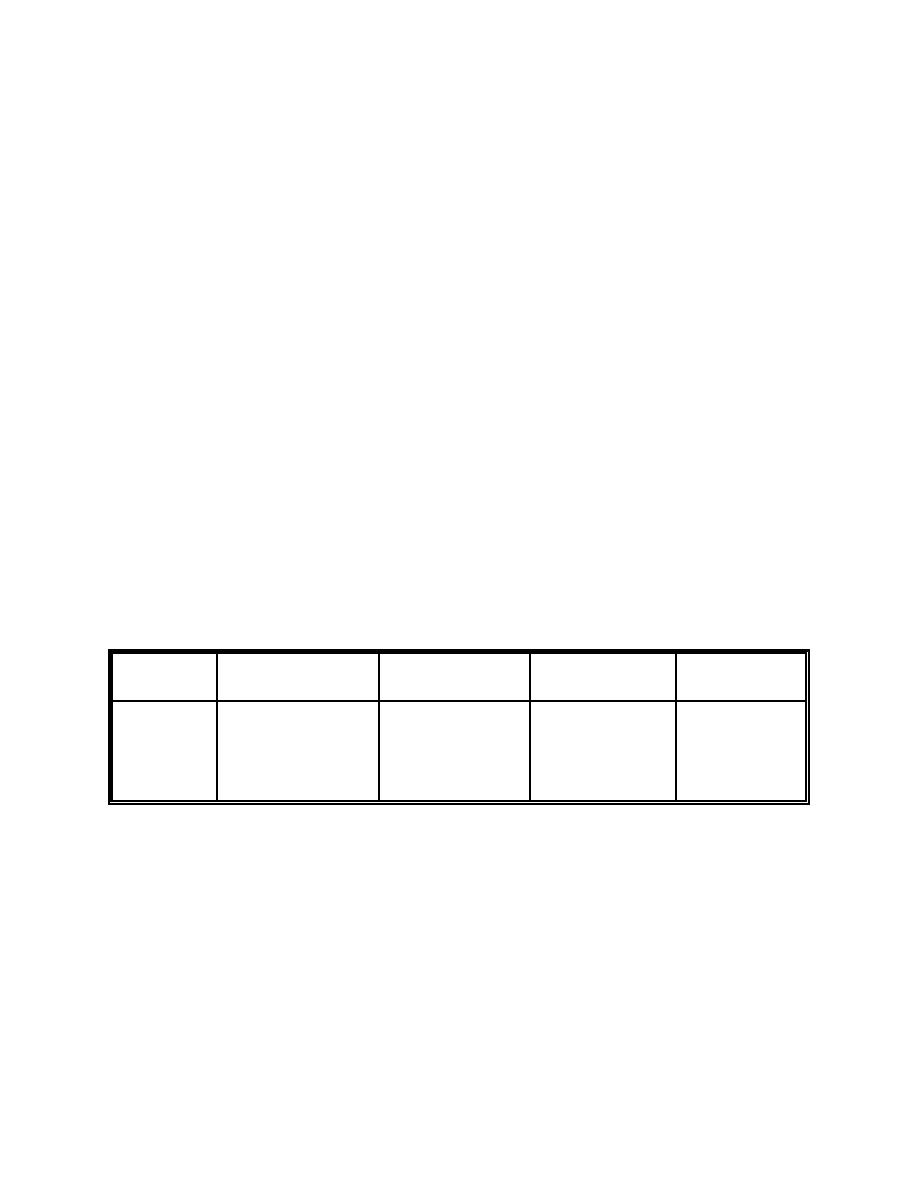
Release topics explored in this example are listed in Table 7-11:
Table 7-11. Reduction Line Example Topics
Liquid
Metal
Powder
Surface
Criticality
- N/A
- Disturbed molten
- Thermal stress
- None
- None
metal surfaces
- Explosive shock
- Self-sustained
effects
oxidation
- Explosive blast
effects
7.3.8.1
Hazard Summary
Plutonium fluoride is received from the hydrofluorination glovebox. A plutonium fluoride
charge, an excess of calcium metal, and a pyrotechnic charge are mixed in a magnesium
oxide crucible. The crucible is placed in a metal reduction can, which is then sealed by
temperature until a thermite-type exothermic reaction is initiated between the plutonium
fluoride and calcium. At temperatures between 1500 oC and 1700 oC, and pressures between
0.34 and 2.8 MPag (50 to 400 psig), the mixture of reaction products is molten and the
Page 7-53
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |