 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Suspension of Liquids From Shallow Pools of Concentrated Heavy Metal Solutions on Stainless Steel |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-3010-94
3.0 Liquids; Aqueous Solutions
3.2.4.2
S u s pen sion of L iq u id s F rom S h allow P ools of C on cen trated H eavy
M etal S olu tion s on S tain less S teel
An indication of the ARF for this type of condition at low velocities can be gained from the
entrainment of plutonium solution in air at velocities from 10 to 100 cm/s passing over the
surface (Mishima, Schwendiman and Radasch, November 1968). The entrainment was from
a very shallow pool (~2 to 4 mm) of limited diameter (~2.5 cm) using a dense solution.
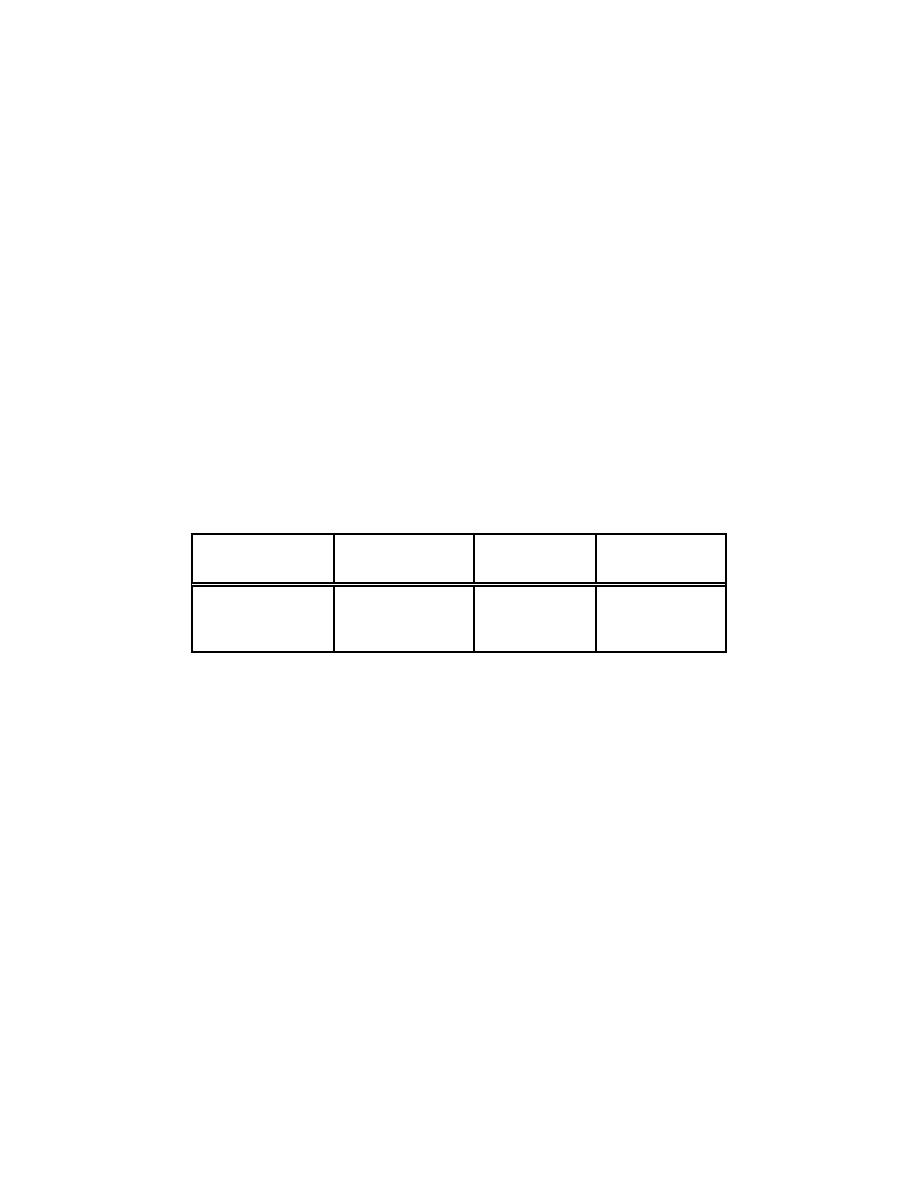
ARF ranged from <2E-10 to 2.5E-9. The ARFs measured are listed in Table 3-10 taken
from Table I in the reference document and found in Appendix A (Table A.1). The
experimental apparatus is shown in Figure A.1.
Table 3-10. M easured ARFs from Shallow Pools of Concentrated
Heavy M etal Salt Solution (0.72 g to 0.82 g Pu, 24-hr sam pling period)
(Table I - M ishim a, Schwendim an and Radasch, Novem ber 1968)
Tem perature,
Air Velocity,
ARF
Rate
C
m /s
ambient
0.1
<1.0E-9
<1.0E-14/s
ambient
0.5
2.5E-9
3.0E-14/s
ambient
1.0
<2.0E-10
<2.0E-15/s
Although the nominal velocities used in these experiments appear to be much lower than
those quoted in subsection 3.2.4.1, the values represent velocities much closer to the surface
(i.e., within cm) than the usual height for meteorological windspeed measurements of 10 m.
For turbulent to laminar flow, the nominal 10 meter windspeed would be a factor of 2 to 10
higher than the values quoted in Table 3-10. The ARRs measured range from 7E-12/hr to
1E-10/hr.
3.2.4.3
E stim ate of th e R esus pen sion of L iq u id s F rom S oil
As will be discussed in Chapter 4, Sehmel and Lloyd (1976a,b) measured resuspension rates
of a powder deposited on a soil surface and deduced that a reasonable value for resuspension
rate was 1E-8/s to 1E-10/s. These values correspond to 4E-5/hr and 4E-7/hr. Liquids are
significantly less susceptible to entrainment than powders.
Page 3-40
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |