 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-1130-98
Module 1: Radiological Fundamentals
Instructor's Notes
c.
Electrons
1) Electrons are in orbit around the nucleus of an atom.
2) Electrons have a negative electrical charge.
3) This negative charge is equal in magnitude to the proton's
positive charge.
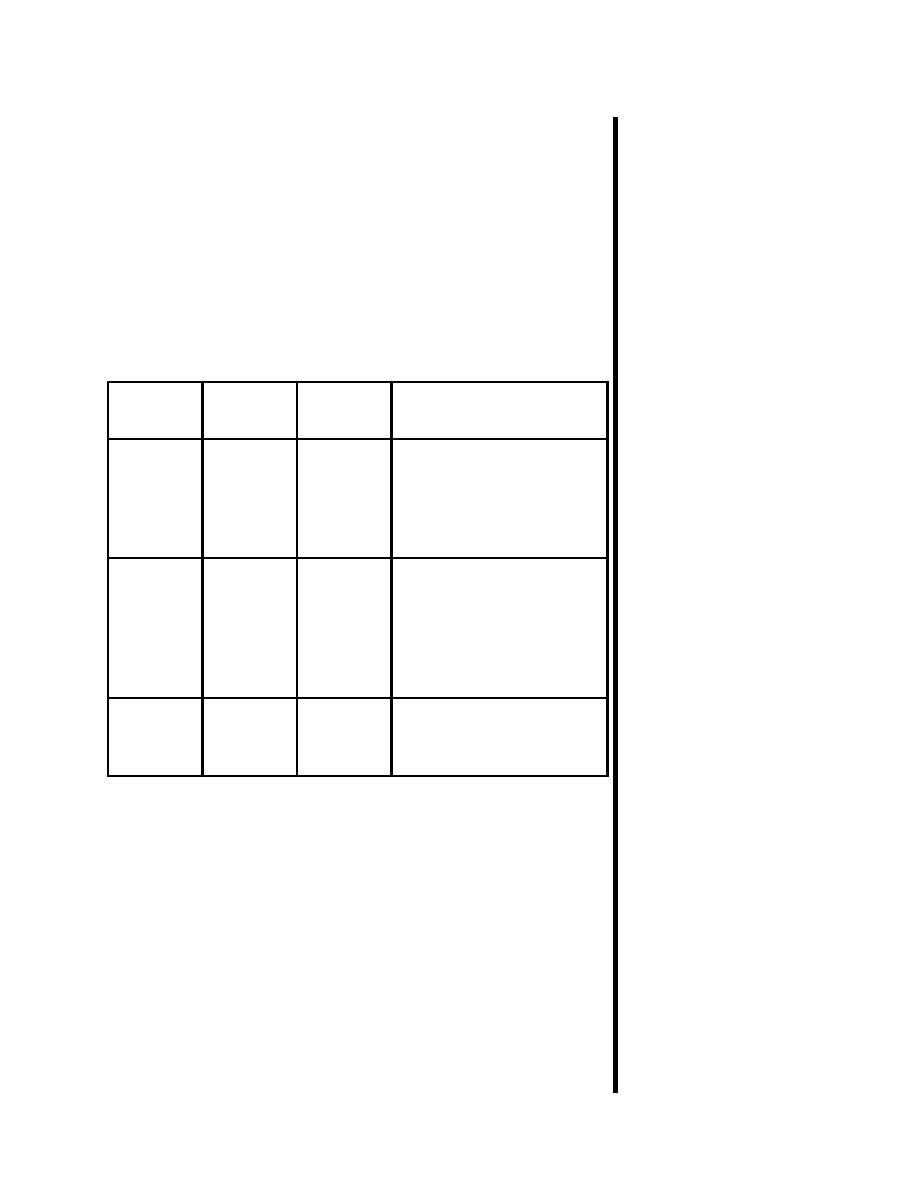
Table 1-1
Basic Particles
3 Basic
Location
Charge
Comments
Particles
Protons
Nucleus
+
Number of protons
(positive)
determines the element. If
the number of protons
changes, the element
changes.
Neutrons
Nucleus
No
Atoms of the same element
Charge
have the same number of
protons, but can have a
different number of
neutrons. This is called an
isotope.
Electrons
Orbit
-
This negative charge is
nucleus
(negative)
equal in magnitude to the
proton's positive charge.
2. Stable and unstable atoms
Only certain combinations of neutrons and protons result in
stable atoms.
a. If there are too many or too few neutrons for a given
number of protons, the nucleus will not be stable.
b. The unstable atom will try to become stable by giving off
excess energy. This energy is in the form of particles or rays
(radiation). These unstable atoms are known as radioactive
atoms.
5
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |