 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
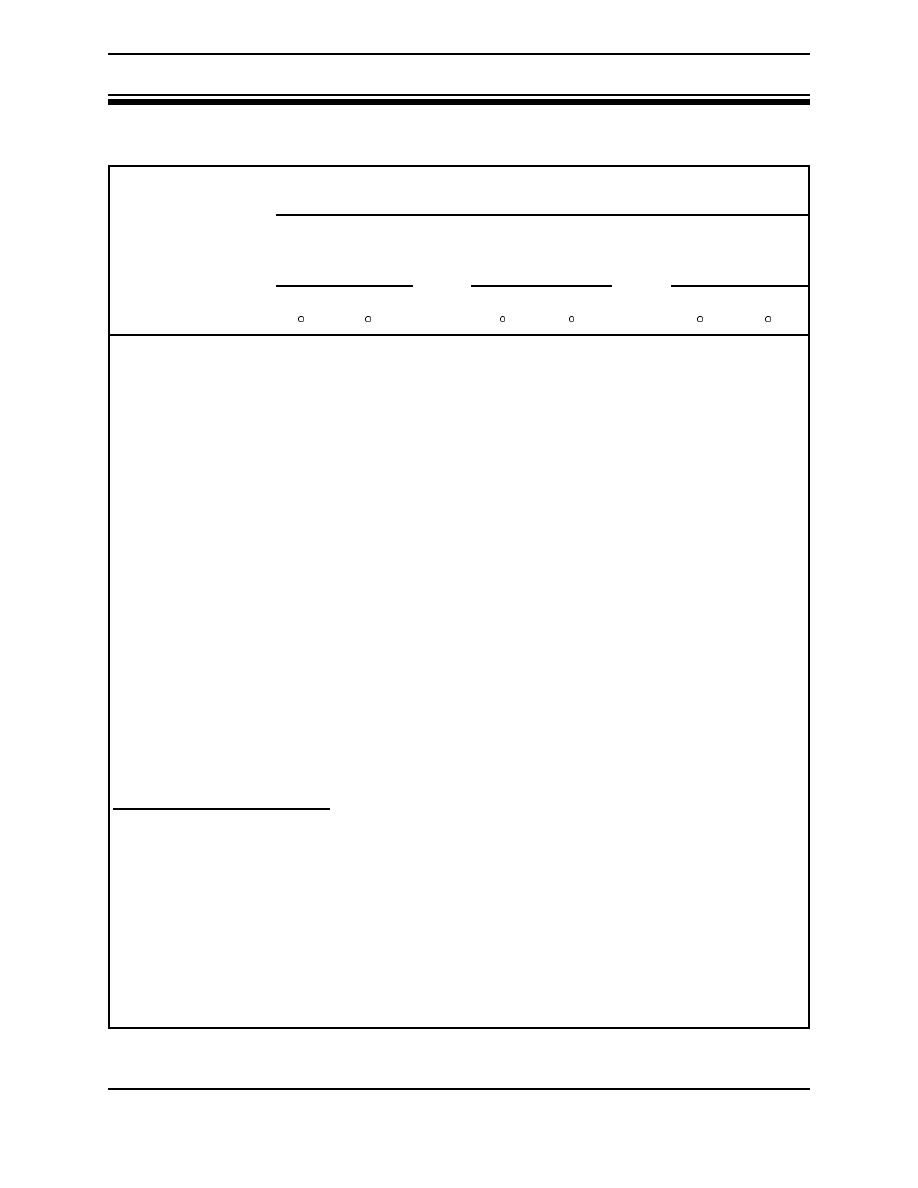
Table 2. Melting, boiling, and ignition temperatures of pure metals in solid form |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|  Spontaneous Heating and Pyrophoricity
DOE-HDBK-1081-94
PYROPHORIC METALS
Table 2. Melting, boiling, and ignition temperatures of pure metals in solid form.1 (From
NFPA Handbook, 17th Edition).
Temperature
Solid metal
Melting point
Boiling point
ignition
Pure metal
F
C
F
C
F
C
1,8322,3
5552,3
Aluminum
1,220
660
4,445
2,452
3472
1752
Barium
1,337
725
2,084
1,140
Calcium
1,548
824
2,625
1,440
1,300
704
Hafnium
4,032
2,223
9,750
5,399
-
-
1,7062
9302
Iron
2,795
1,535
5,432
3,000
Lithium
367
186
2,437
1,336
356
180
Magnesium
1,202
650
2,030
1,110
1,153
623
Plutonium
1,184
640
6,000
3,315
1,112
600
1562
692
Potassium
144
62
1,400
760
2394
1154
Sodium
208
98
1,616
880
1,3282
7202
Strontium
1,425
774
2,102
1,150
9322
5002
Thorium
3,353
1,845
8,132
4,500
Titanium
3,140
1,727
5,900
3,260
2,900
1,593
6,9002,5
3,8152,5
Uranium
2,070
1,132
6,900
3,815
1,6522
9002
Zinc
786
419
1,665
907
2,5522
1,4002
Zirconium
3,326
1,830
6,470
3,577
1. Variation of test conditions may produce different results.
2. Ignition in oxygen.
3. Spontaneous ignition in moist air.
4. Above indicated temperature.
5. Below indicated temperature.
Rev. 0
Page 21
Pyrophoricity
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |