 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-1130-98
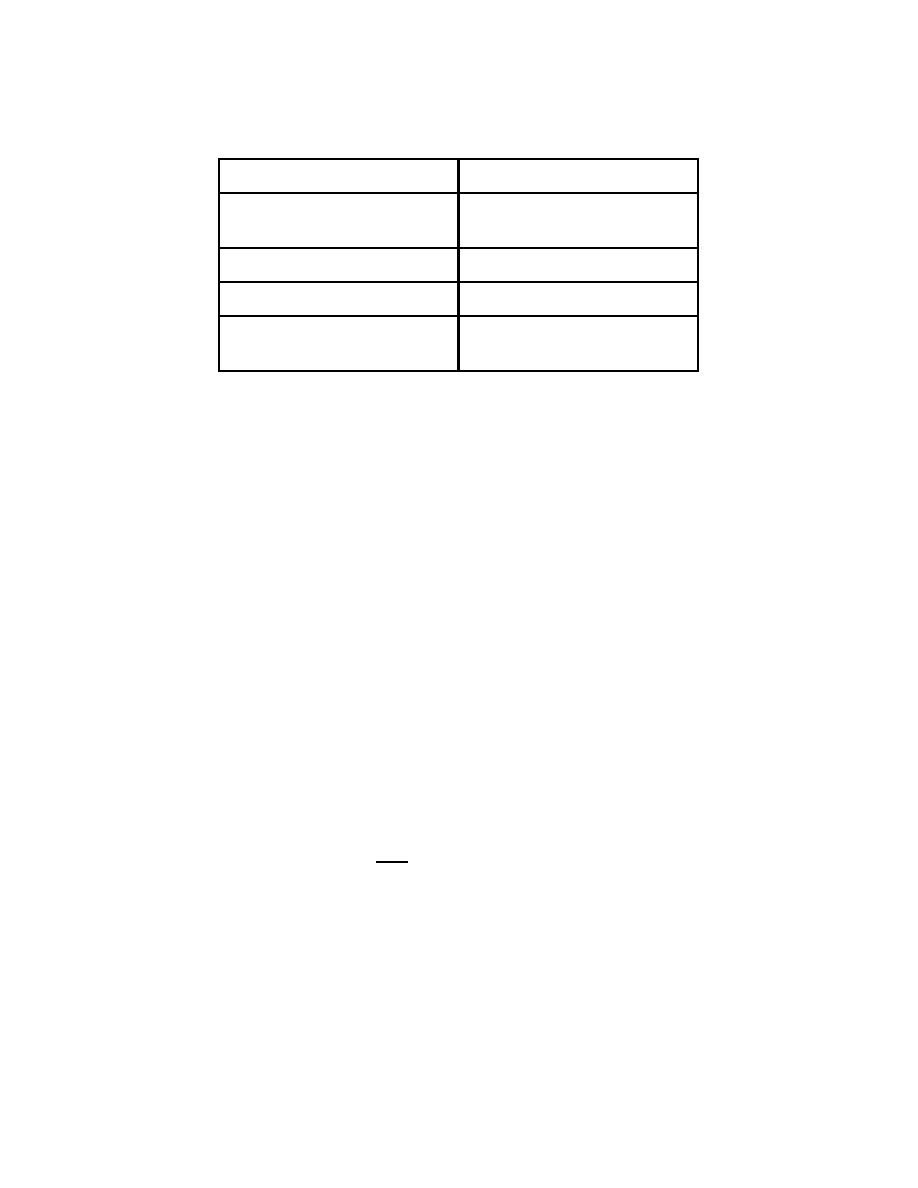
Table 2-1
Prompt Biological Effects
Dose (rem)
Effect
0-25
None detectable through
symptoms or routine blood tests.
25-100
Changes in blood.
100-300
Nausea, anorexia.
300-600
Diarrhea, hemorrhage, and
possible death
2) Delayed Effects
Delayed effects may result from either a single large acute overexposure or
from continuing low-level chronic exposure. Cancer in its various forms is
the most important potential delayed effect of radiation exposure. Other
effects noted include cataracts, life shortening and, for individuals exposed
in the womb, lower IQ test scores.
b. Heritable Effects
A heritable effect is a physical mutation or trait that is passed on to offspring.
In the case of heritable effects, the parental individual has experienced damage
to some genetic material in the reproductive cells and has passed the damaged
genetic material onto offspring.
1) Heritable effects from radiation have never been observed in humans but
are considered possible. They have been observed in studies of plants and
animals.
2) Heritable effects have not been found in the 77,000 Japanese children born
to the survivors of Hiroshima and Nagasaki (these are children who were
conceived after the atom bomb -- i.e., heritable effects). Studies have
followed these children, their children, and their grandchildren.
4. Factors affecting biological damage due to exposure to radiation
a. Total dose
22
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |