 |
|||
|
Page Title:
The Radioactive Decay of Tritium |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-1132-99
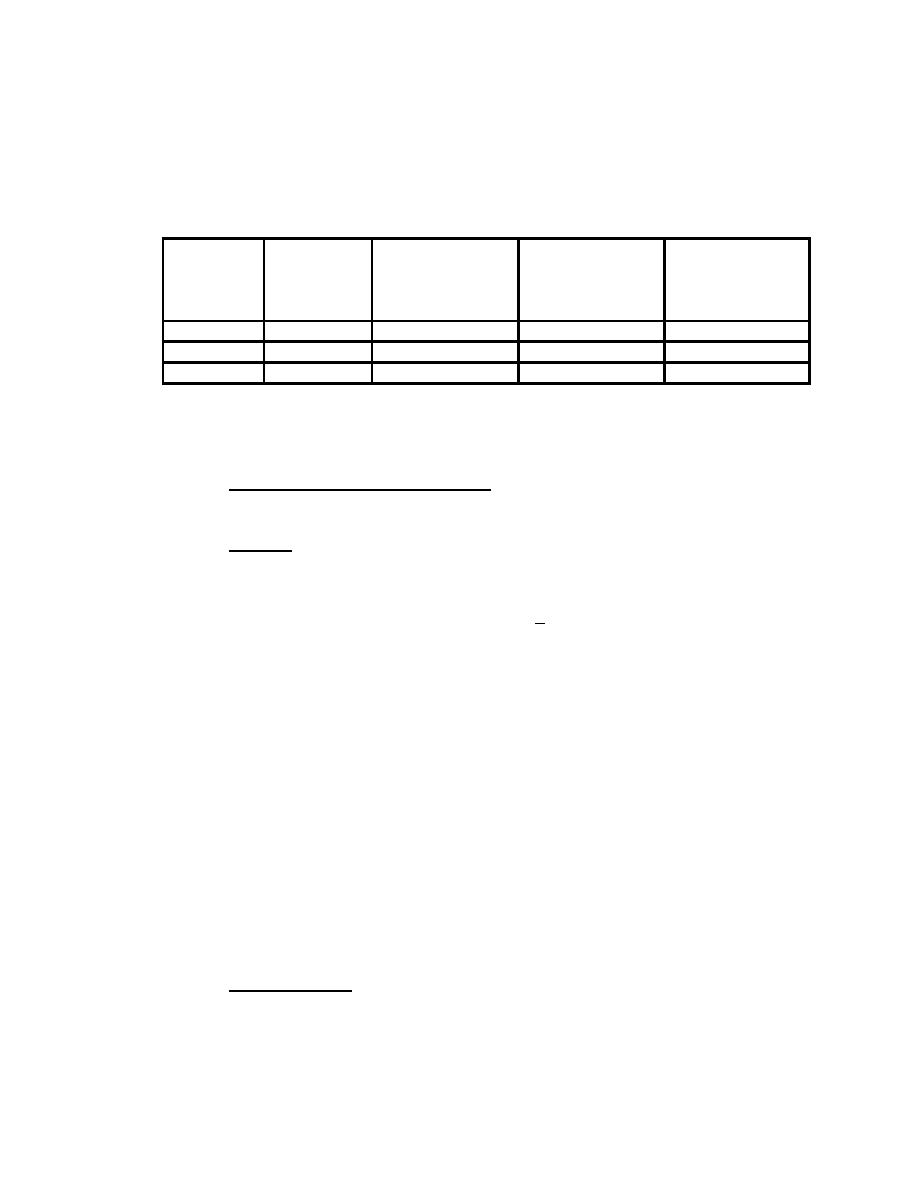
The names, commonly used symbols, atomic masses, and relative natural
Natural
Name
Chemical
Atomic Mass
Natural
Abundance
Symbol
Abundance
(x:H Ratio)
(Percent)
Protium
H
1.007 825 03
99.985 %
1:1
Deuterium
D
2.014 101 78
0.015 %
1:6,600
1:1017
Tritium
T
3.016 049 26*
very low
* Calculated
2.10.4
The Radioactive Decay of Tritium .
Generic . As the lightest of the pure beta emitters, tritium decays with the
emission of a low-energy beta particle and an anti-neutrino; i.e.,
Η e + β + ν.
6
-
Η
3
3
(2)
1
2
Tritium decays with a half-life of 12.3232 0.0043 mean solar years or, using
365.2425 mean solar (days) per mean solar year, 4,500.96 1.57 days. The
specific activity of tritium is approximately 9,619 Ci/g, and/or 1.040 10 -4 g/Ci.
In addition, the activity density (i.e., the specific activity per unit volume) for
tritium gas (T2) is 2.589 Ci/cm3, under standard temperature and pressure
(STP) conditions (i.e., 1 atmosphere of pressure at 0 EC), and/or 2.372 Ci/cm3
at 25EC. Under STP conditions, it can also be shown that these values
translate to 58,023 Ci/g-mole and 29,012 Ci/g-atom, respectively.
Beta Emissions. Beta particles interact with matter by colliding with bound
electrons in the surrounding medium. In each collision, the beta particle loses
energy as electrons are stripped from molecular fragments (ionization) or
promoted to an excited state (bremsstrahlung production). Because the rate
I-90
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |