 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Table 1. Summary of Root Cause Methods |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
| 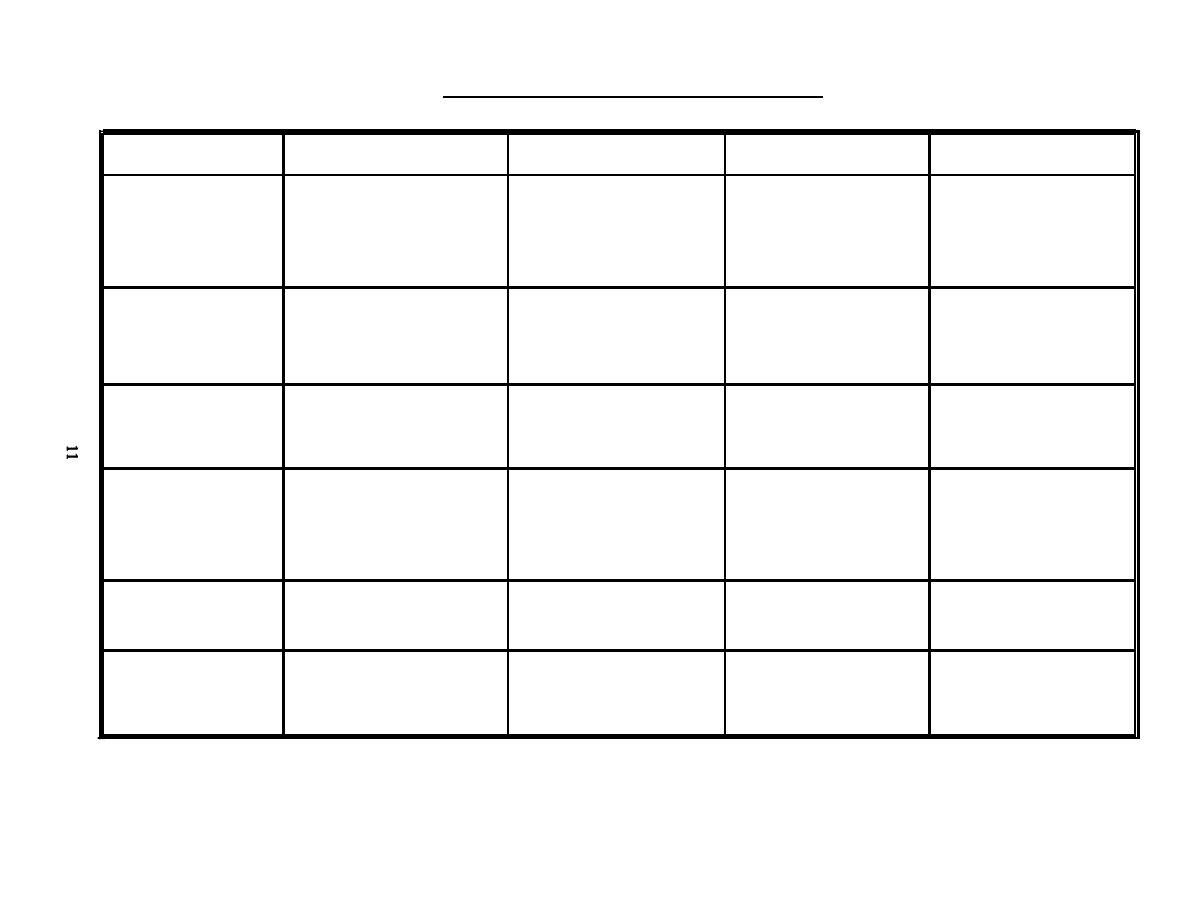 TABLE 1. SUMMARY OF ROOT CAUSE METHODS
REMARKS
METHOD
WHEN TO USE
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
Events and Causal Factor
Use for multi-faceted problems
Provides visual display of
Requires a broad perspective
Time-consuming and requires
Analysis
with long or complex causal
of the event to identify
analysis process. Identifies
familiarity with process to
unrelated problems. Helps to
factor chain.
probable contributors to the
be effective.
identify where deviations
condition.
occurred from acceptable
methods.
Change Analysis
Use when cause is obscure.
A singular problem technique
Simple 6-step process.
Limited value because of the
Especially useful in evaluating
that can be used in support
danger of accepting wrong,
equipment failures.
of a larger investigation.
"obvious" answer.
All root causes may not be
identified.
This process is based on the
Barrier Analysis
Use to identify barrier and
Provides systematic approach.
Requires familiarity with
equipment failures and
MORT Hazard/Target Concept.
process to be effective.
procedural or administrative
problems.
MORT/Mini-MORT
If this process fails to
Use when there is a shortage of
Can be used with limited prior
May only identify area of
experts to ask the right
training. Provides a list of
cause, not specific causes.
identify problem areas, seek
questions and whenever the
additional help or use cause-
questions for specific control
problem is a recurring one.
and management factors.
and-effect analysis.
Helpful in solving programmatic
problems.
Human Performance
Use whenever people have been
Thorough analysis.
Requires HPE training.
None if process is closely
Evaluations (HPE)
identified as being involved in
followed.
the problem cause.
Kepner-Tregoe
Use for major concerns where
Highly structured approach
Requires Kepner-Tregoe
More comprehensive than may
all spects need thorough
focuses on all aspects of the
training.
be needed.
analysis.
occurrence and problem
resolution.
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |