 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
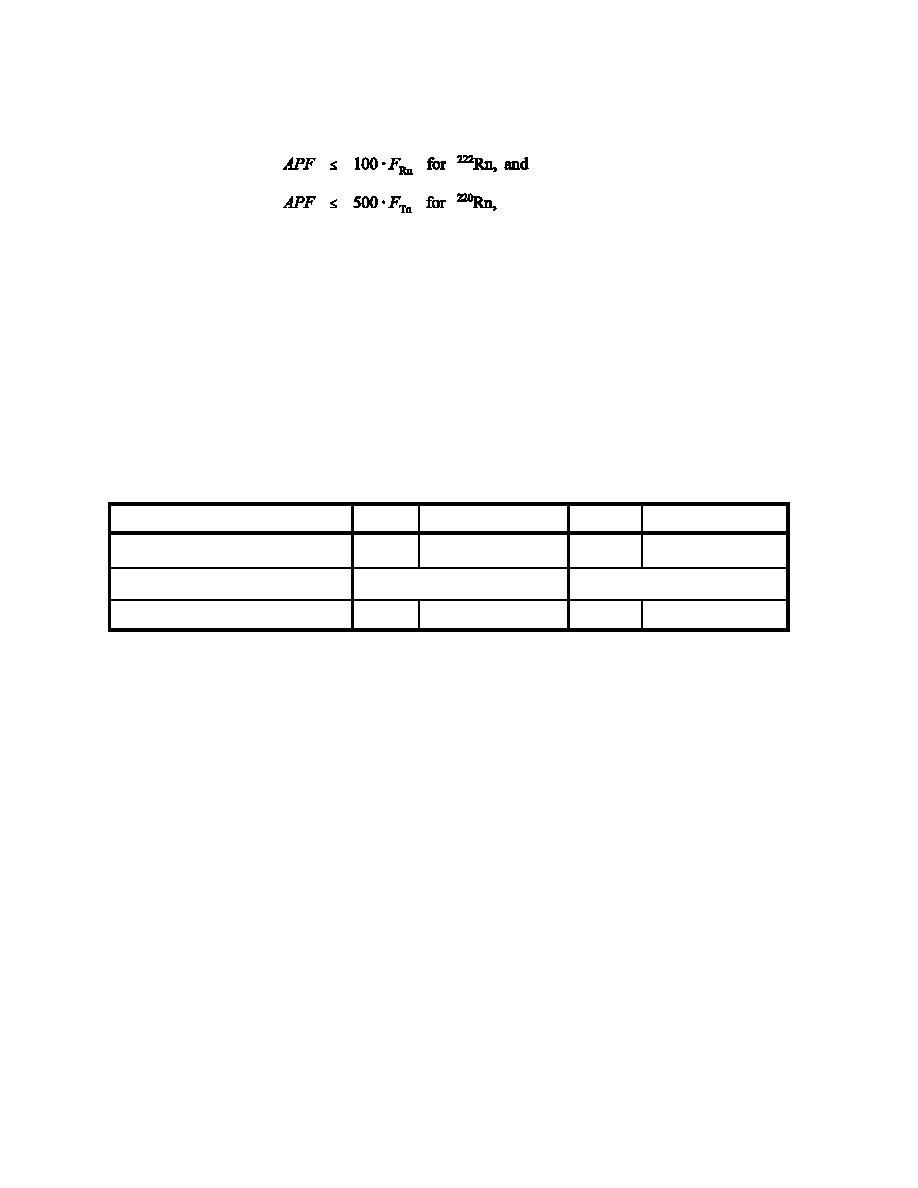
Table VI. Three Options for Assigned Protection Factors for Rn, Tn, and Their Progeny |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-STD-1121-98
(41)
with the proviso that the APF cannot be less than 1.
Using the default values of 0.4 and 0.04 as examples, APFs can be no more than 40 for radon taken
together with its progeny, or 20 for thoron taken together with its progeny, regardless of the respirator's
performance for radon or thoron progeny.
The third option is to follow a recommendation by the National Institute of Occupational Safety and
Health (NIOSH). NIOSH has recommended that an APF of no more than 10 be allowed for respirator use
in underground mines due to the observation that workers do not use respirators more than 90% of the
time (NIOSH 1987). Similarly, the ICRP has recommended a protection factor of no more than 10 in
paragraphs 69 and 71 (ICRP 1986a), for practical reasons.
Table VI. Three Options for Assigned Protection Factors for Rn, Tn, and Their Progeny
Option
Radon
Radon Progeny
Thoron
Thoron Progeny
Measure Gas and Progeny
1
ANSI Z88.2-1992
1
ANSI Z88.2-1992
1 # APF # 100 A FRn
1 # APF # 500 A FTn
Eq. Factor, Gas Measurement
NIOSH/ICRP
1
10
1
10
For airline supplied-air respirators, it is important to ensure that the intake air is filtered of radon
progeny and free of radon gas. Bottled-air respirators in which the air has been aged for 30 or more days
may be assumed to be free of radon and radon progeny.
7.5.8 Determination of Radon and Thoron Background
The background concentration used should be the best available estimate of the average
concentration that would have existed without the activity or source. For distributed sources of radon, it
is suggested that background be determined in accordance with DOE/EH-01737, Environmental
One method of determining background is through measurements made before the commencement
of the activity or from measurements made in other unaffected parts of the same building (indoors) or
from measurements made at least 400 m (.1/4 mile) away from any known local source and/or up wind
(outdoors). A site-specific background should be used whenever possible. However, if determination of
the site-specific background is not feasible, a community-wide average may be used for up to one year
until local measurements have been made. If neither of these is practicable, then background values of
0.006 WL for radon progeny and 0.002 WL for thoron progeny may be used indoors and 0.002 WL for
radon progeny and 0.001 WL for thoron progeny may be used outdoors (see Table VII).
87
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |