 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
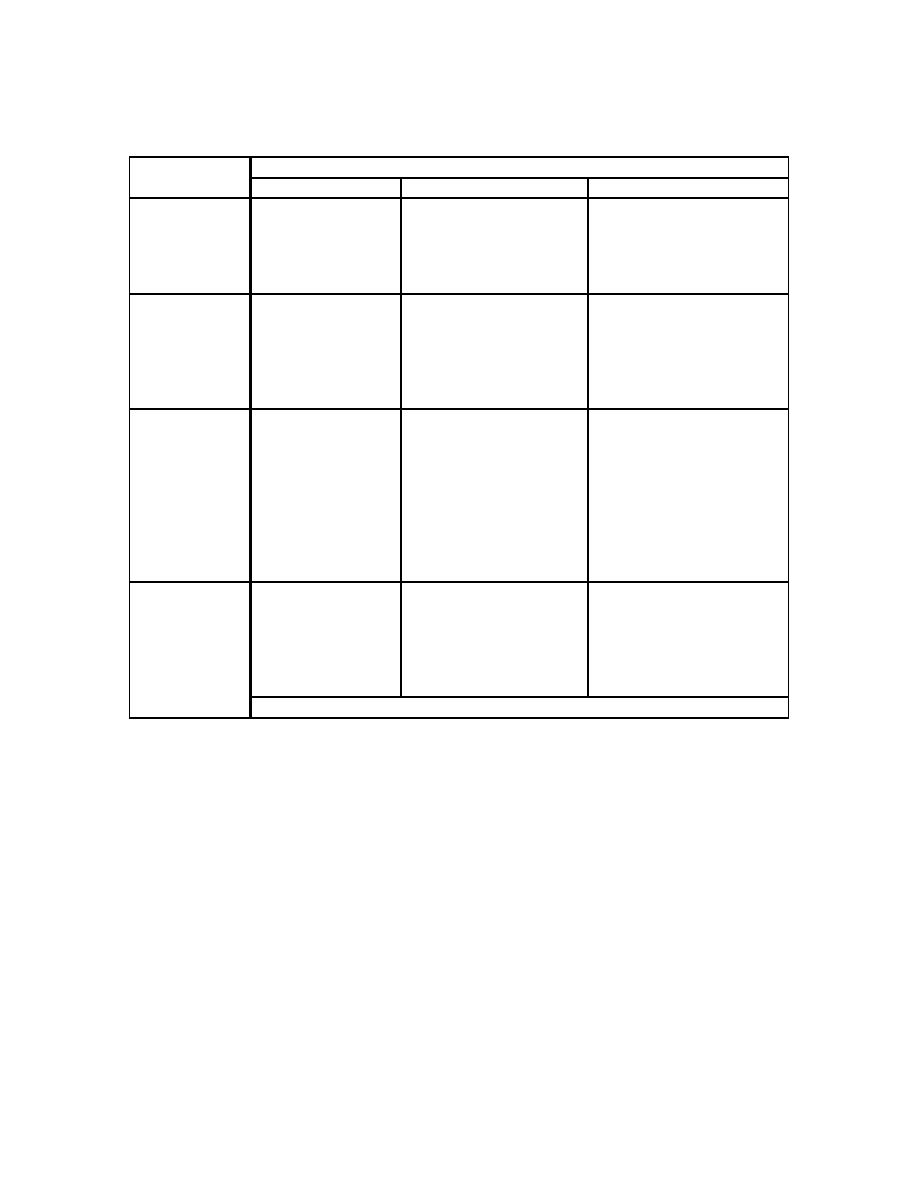
Specificity of Administrative Controls |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-STD-1120-2005/Vol. 1
independent readings, and assurances that calculations needed within administrative controls are
independently verified).
Specificity of Administrative Controls→
General
More Specific
Very Specific
Description of
General
Defined safety
Defined Limits and
administrative
Commitment to
management program
commitments
control
Implement a Safety activities or elements
Management
and/or Operational
Program
Parameters
When To
SSCs are available
SSCs are available, but
SSCs are unavailable or not
Apply
and used to control are not completely
cost beneficial (i.e., short
the hazard
effective in controlling a
duration decommissioning)
hazard
and only administrative
controls are used to control
the hazard
Level of
ACs contribute to
Important to safety;
Primary or contributing
Importance of
safety by ensuring
needed to protect an
control selected from the
administrative
programmatic
initial condition in the
hazard/accident analysis as
control-
elements are
hazard analysis or
a major
available
selected from the
mitigative/preventive
hazard/accident analysis
feature(s)
to supplement other
mitigative/preventive
features
Example
"A combustible
"The fire protection
"Combustible wastes shall
control program
program shall ensure that
be maintained below 100
shall be established
combustible wastes are
pounds in the facility"
for the facility"
removed daily during
TRU waste packaging
activities"
Severity of Hazards→
Figure 1. Specificity of Administrative Controls
2.5
Change Control Process
During the performance of decommissioning work, changes may be necessary to facility systems
or work plans that are not anticipated. In order to ensure that the safety basis is current,
adequate, and documented, it is important that a change control process be developed that
considers the significance of proposed changes and links to the USQ process to determine if
DOE approval of the change will be necessary.
Unanticipated changes or discovery of new information may also affect a condition, parameter,
or assumption that helped support the basis for downgrading a facility below hazard category 3.
Such changes should be subjected to a management of change process to evaluate potential
impact on the approved safety basis that supported a downgrade. Violation of certain
assumptions and controls could invalidate the downgrade such as changes in radionuclide
material inventory, form of material, dispersibility (e.g., changes in container storage or energy
2-5
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |