 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Table 1-4 Gamma Rays/X-Rays |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|  DOE-HDBK-1130-98
Module 1: Radiological Fundamentals
Instructor's Notes
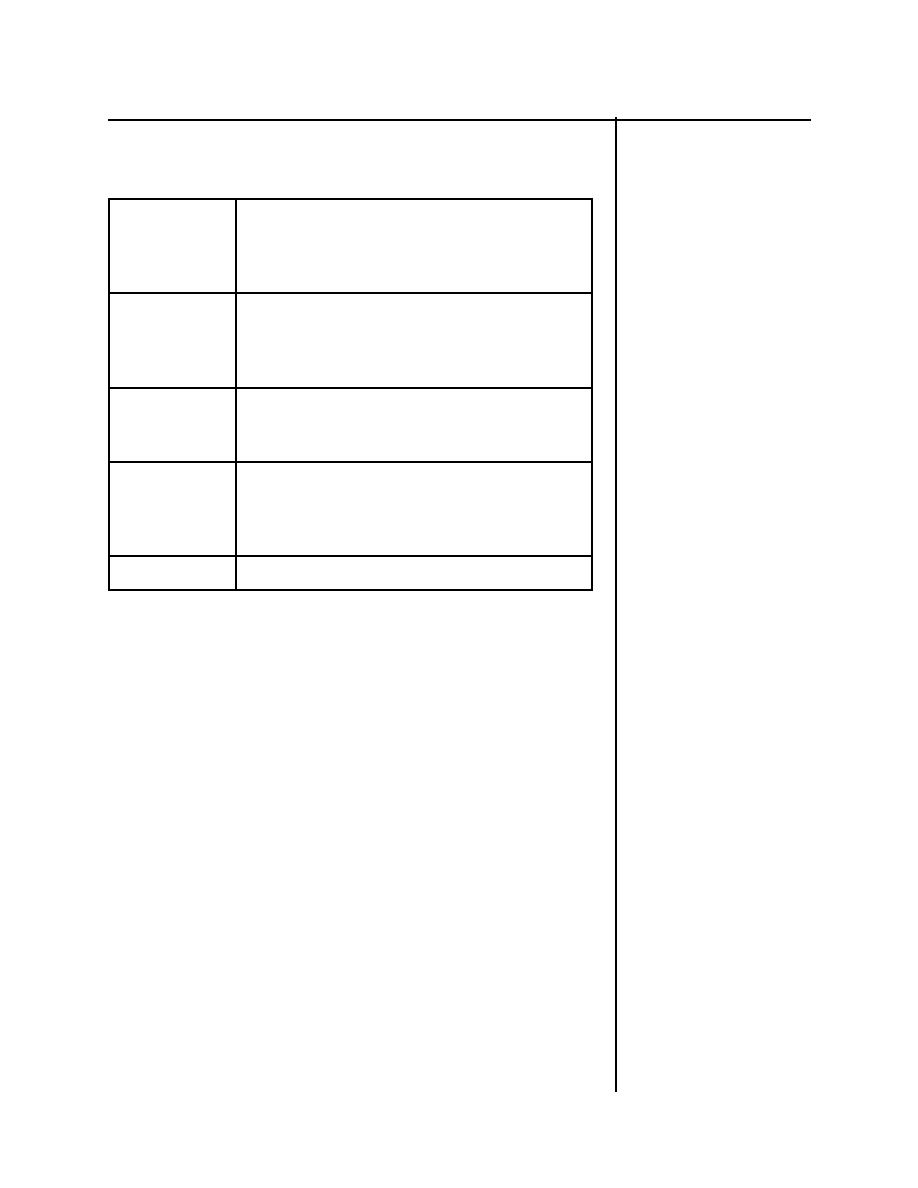
Table 1-4
Gamma Rays/X-Rays
No mass.
Physical
No charge.
Characteristic
Electromagnetic wave or photon.
s
Similar (difference is the place of origin).
Range in air is very far.
It will easily go several hundred feet.
Range
Very high penetrating power since it has no
mass and no charge.
Concrete.
Water.
Shielding
Lead.
Whole body exposure.
The hazard may be external and/or internal.
This depends on whether the source is inside
Hazard
or outside the body.
Insert facility-specific information.
Sources
4. Neutrons
EO6 Identify the four basic
types of ionizing radiation
a.
Physical characteristics
and the following for each
type:
a. Physical characteristics
from the nucleus.
b. Range
c. Shielding
2) A neutron has mass, but no electrical charge.
d. Biological hazards
e. Sources
3) An interaction can occur as the result of a collision
between a neutron and a nucleus. The nucleus recoils
due to the energy imparted by the neutron and ionizes
other atoms. This is called "secondary ionization."
4) Neutrons may also be absorbed by a nucleus. This is
called neutron activation. A charged particle or
gamma ray may be emitted as a result of this
interaction. The emitted radiation can cause ionization
in other atoms.
13
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |