 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Table 4-2 Design Basis Flood Events |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
| 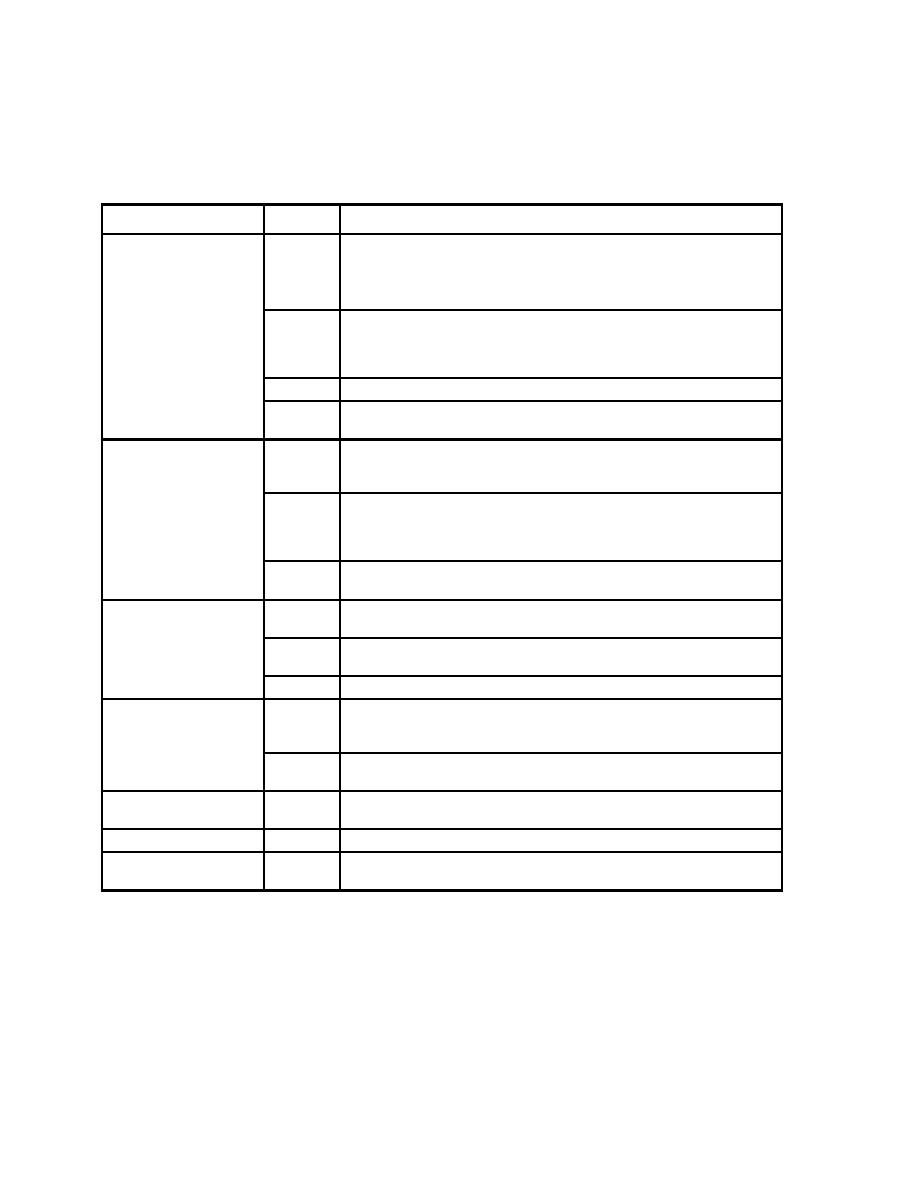 DOE-STD-1020-2002
Table 4-2 Design Basis Flood Events
Primary Hazard
Case No.
Event Combinations*
River Flooding
1
Peak flood elevation. Note: The hazard analysis for river flooding
should include all contributors to flooding, including releases from
upstream dams, ice jams, etc. Flooding associated with upstream-dam
failure is included in the dam failure category.
2
Wind-waves corresponding, as a minimum to the 2-year wind acting in
the most favorable direction (Ref. 4-2), coincident with the peak flood or
as determined in a probabilistic analysis that considers the joint
occurrence of river flooding and wind generated waves.
3
Ice forces (Refs. 4-2 and 4-3) and Case 1.
4
Evaluate the potential for erosion, debris, etc. due to the primary
hazard.
Dam Failure
1
All modes of dam failure must be considered (i.e., overtopping,
seismically induced failure, random structural failures, upstream dam
failure, etc.)
2
Wind-waves corresponding, as a minimum to the 2-year wind acting in
the most favorable direction (Ref. 4-2), coincident with the peak flood or
as determined in a probabilistic analysis that considers the joint
occurrence of river flooding and wind generated waves.
3
Evaluate the potential for erosion, debris, etc. due to the primary
hazard.
Local Precipitation
1
Flooding based on the site runoff analysis shall be used to evaluate the
site drainage system and flood loads on individual facilities.
2
Ponding on roof to a maximum depth corresponding to the level of the
secondary drainage system.
3
Rain and snow, as specified in applicable regulations.
Storm Surge, Seiche
1
Tide effects corresponding to the mean high tide above the MLW** level
(due to hurricane,
(if not included in the hazard analysis).
seiche, squall lines, etc.)
2
Wave action and Case 1. Wave action should include static and
dynamic effects and potential for erosion (Ref. 4-2).
Levee or Dike Failure
1
Should be evaluated as part of the hazard analysis if overtopping and/or
failure occurs.
Snow
1
Snow and drift roof loads as specified in applicable regulations.
Tsunami
1
Tide effects corresponding to the mean high tide above the MLW** level
(if not included in the hazard analysis).
* Events are added to the flood level produced by the primary hazard.
** MLW-Mean Low Water.
The DBFL for a SSC for a flood hazard (e.g., river flooding, local precipitation) is
defined in terms of:
1.
Peak-hazard level (e.g., flow rate, depth of water) corresponding to the
mean, hazard annual exceedance probability (see Table 4-1), including the
4-3
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |